Java Memory Allocation.
Memory allocation is a process by which computer programs and services are assigned with physical or virtual memory space.
In Java, memory management is the process of allocation and de-allocation of objects, called Memory management. Java does memory management automatically. Java uses an automatic memory management system called a garbage collector. Thus, we are not required to implement memory management logic in our application. Java memory management divides into two major parts:
- JVM Memory Structure
- Working of the Garbage Collector
Types of Memory areas allocated by the JVM:
JVM creates various run time data areas in a heap. These areas are used during the program execution. The memory areas are destroyed when JVM exits, whereas the data areas are destroyed when the thread exits.
All these functions take different forms of the memory structure.
The memory in the JVM divided into 5 different parts:
Let’s see about them in brief:
- Class Loader:It is a subsystem of JVM which is used to load class files.It is mainly responsible for three activities.
- Loading
- Linking
- Initialization
- Class(Method) Area: It stores class level data of every class such as the runtime constant pool, field and method data, the code for methods.
- Heap: It is used to allocate memory to objects at run time
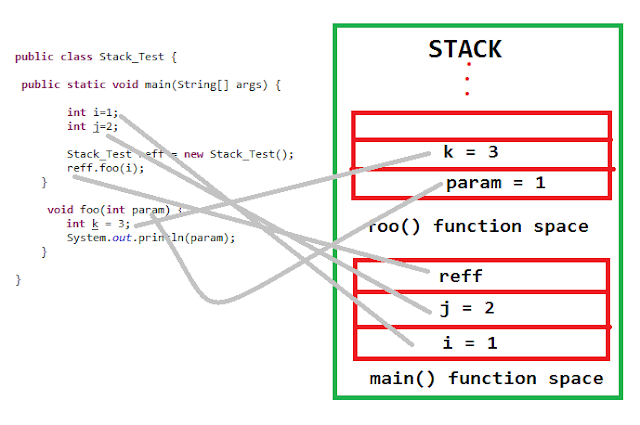
- Stack:
- Each thread has a private JVM stack, created at the same time as thread. It is used to store data and partial results which will be needed while returning value for method and performing dynamic linking.
- Java
Stack stores frames and a new frame is created each time at every
invocation of the method.
A frame is destroyed when its method invocation completes - Program Counter Register: Each JVM thread which carries out the task of a specific method has a program counter register associated with it. The non-native method has a PC which stores the address of the available JVM instruction whereas, in a native method, the value of the program counter is undefined. PC register is capable of storing the return address or a native pointer on some specific platform.
- Native method Stacks: Also called as C stacks, native method stacks are not written in Java language. This memory is allocated for each thread when its created And it can be of a fixed or dynamic nature.


Comments
Post a Comment