Inheritance in Java
Child Class:
The class that extends the features of another class is known as child class,
sub class or derived class.
Parent Class:
The class whose properties and functionalities are used(inherited) by another
class is known as parent class, super class or Base class.
Syntax: Inheritance in
Java
class Animal
{
eat() method
sleep() method
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
bark() method
}
In Java, we use
the extends keyword to inherit from a class.
Here, we have inherited the Dog class from
the Animal class.
The Animal is the superclass (parent class or base class),
and the Dog is a
subclass (child class or derived class). The subclass inherits the fields and
methods of the superclass.
Note:
The derived class inherits all the members and methods that
are declared as public or protected. If the members or methods of super class
are declared as private then the derived class cannot use them directly. The
private members can be accessed only in its own class. Such private members can
only be accessed using public or protected getter and setter methods of super
class as shown in the example below
The important point to note in the above example is that the child class is able to access the private members of parent class through protected methods of parent class. When we make a instance variable(data member) or method protected, this means that they are accessible only in the class itself and in child class. These public, protected, private etc. are all access specifiers and we will discuss them in the coming tutorials.
1) Single Inheritance
2) Multiple Inheritance
3) Multilevel
Inheritance
4) Hierarchical
Inheritance
5) Hybrid Inheritance
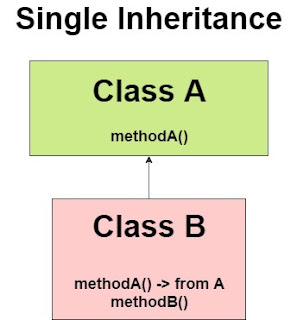
1) Single Inheritance
Single inheritance is
damn easy to understand. When a class extends another one class only then we
call it a single inheritance. The below flow diagram shows that class B
extends only one class which is A. Here A is a parent class of B and B would be
a child
class of A.
Single Inheritance example
program in Java
Class A
{
public void methodA()
{
System.out.println("Base class method");
}
}
Class B extends A
{
public void methodB()
{
System.out.println("Child class method");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj = new B();
obj.methodA(); //calling super class method
obj.methodB(); //calling local method
}
}
2) Multiple Inheritance
“Multiple Inheritance” refers to the concept of one
class extending (Or inherits) more than one base class. The inheritance we
learnt earlier had the concept of one base class or parent. The problem with
“multiple inheritance” is that the derived class will have to manage the dependency
on two base classes.
Note
2: Most of the new OO languages like Small Talk,
Java, C# do not support Multiple inheritance.
Multiple Inheritance is supported in C++.
3)
Multilevel Inheritance
Multilevel inheritance refers
to a mechanism in OO technology where one can inherit from a derived class,
thereby making this derived class the base class for the new class. As you can
see in below flow diagram C is subclass or child class of B and B is a child
class of A.
It’s pretty clear with the diagram that in
Multilevel inheritance there is a concept of grand parent class. If we take the
example of this diagram, then class C inherits class B and class B inherits
class A which means B is a parent class of C and A is a parent class of B. So
in this case class C is implicitly inheriting the properties and methods of
class A along with class B that’s what is called multilevel inheritance.
Multilevel Inheritance
Example
In
this example we have three classes – Car, Maruti and Maruti800. We
have done a setup – class Maruti extends Car and class Maruti800 extends Maruti. With the help of this
Multilevel hierarchy setup our Maruti800 class is able to use the methods of
both the classes (Car and Maruti).
class Car{
public Car()
{
System.out.println("Class Car");
}
public void vehicleType()
{
System.out.println("Vehicle Type: Car");
}
}
class Maruti extends Car{
public Maruti()
{
System.out.println("Class Maruti");
}
public void brand()
{
System.out.println("Brand: Maruti");
}
public void speed()
{
System.out.println("Max: 90Kmph");
}
}
public class Maruti800 extends Maruti{
public Maruti800()
{
System.out.println("Maruti Model: 800");
}
public void speed()
{
System.out.println("Max: 80Kmph");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Maruti800 obj=new Maruti800();
obj.vehicleType();
obj.brand();
obj.speed();
}
}
Output:
Class Car
Class Maruti
Maruti Model: 800
Vehicle Type: Car
Brand: Maruti
Max: 80Kmph
Multilevel Inheritance example
program in Java
Class X
{
public void methodX()
{
System.out.println("Class X method");
}
}
Class Y extends X
{
public void methodY()
{
System.out.println("class Y method");
}
}
Class Z extends Y
{
public void methodZ()
{
System.out.println("class Z method");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Z obj = new Z();
obj.methodX(); //calling grand parent class method
obj.methodY(); //calling parent class method
obj.methodZ(); //calling local method
}
}
4) Hierarchical Inheritance
In
such kind of inheritance one class is inherited by many sub classes. In below example class B,C
and D inherits the
same class A. A is parent
class (or base class) of B,C & D.
When
more than one classes inherit a same class then this is called hierarchical
inheritance. For example class B, C and D extends a same class A. Lets see the
diagram representation of this:
As
you can see in the above diagram that when a class has more than one child
classes (sub classes) or in other words more than one child classes have the
same parent class then this type of inheritance is
known as hierarchical inheritance.
class A
{
public void methodA()
{
System.out.println("method of Class A");
}
}
class B extends A
{
public void methodB()
{
System.out.println("method of Class B");
}
}
class C extends A
{
public void methodC()
{
System.out.println("method of Class C");
}
}
class D extends A
{
public void methodD()
{
System.out.println("method of Class D");
}
}
class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj1 = new B();
C obj2 = new C();
D obj3 = new D();
//All classes can access the method of class A
obj1.methodA();
obj2.methodA();
obj3.methodA();
}
}
Output:
method of Class A
method of Class A
method of Class A
5) Hybrid
Inheritance
In
simple terms you can say that Hybrid inheritance is a combination of Single and Multiple inheritance. A
typical flow diagram would look like below. A hybrid inheritance can be
achieved in the java in a same way as multiple inheritance can be!!
Using interfaces. yes you heard it right. By using interfaces you can have multiple as
well as hybrid
inheritance in Java.
A hybrid inheritance is a combination of more than one types
of inheritance. For example when class A and B
extends class C & another class D extends class A then this is a hybrid
inheritance, because it is a combination of single and hierarchical
inheritance. Let me show you this diagrammatically:
Hybrid Inheritance in
Java
It seems that because of this
diagram people are finding it difficult to understand this topic because this
diagram shows combination of hierarchical and multiple inheritance and multiple
inheritance is not supported in java.
The diagram is just for the representation, since multiple inheritance is not
possible in java, It is not correct to show that as a part of hybrid
inheritance. I will update the diagram whenever I get the time. You can refer
the example that I have given at the beginning of post representing combination
of single and hierarchical inheritance
Program: This example is just to
demonstrate the hybrid inheritance in Java. Although this example is
meaningless, you would be able to see that how we have implemented two types of
inheritance(single and hierarchical) together to form hybrid inheritance.
Class A and B extends class C → Hierarchical inheritance
Class D extends class A → Single inheritance
class C
{
public void disp()
{
System.out.println("C");
}
}
class A extends C
{
public void disp()
{
System.out.println("A");
}
}
class B extends C
{
public void disp()
{
System.out.println("B");
}
}
class D extends A
{
public void disp()
{
System.out.println("D");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
D obj = new D();
obj.disp();
}
}
Output:
D
The aim of inheritance is to provide the reusability of code so that a class has to write only the unique features and rest of the common properties and functionalities can be extended from the another class.
The biggest advantage of Inheritance is
that the code that is already present in base class need not be rewritten in
the child class.
This
means that the data members(instance variables) and methods of the parent class
can be used in the child class as.
.






Comments
Post a Comment