Encapsulation in Java
What is encapsulation?
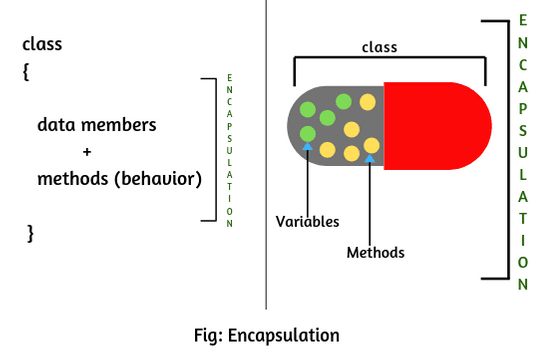
Encapsulation
is defined as the wrapping up of data under a single unit. It is the mechanism
that binds together code and the data it manipulates. Other way to think about
encapsulation is, it is a protective shield that prevents the data from being
accessed by the code outside this shield.
- Technically in encapsulation, the variables or data of a class is hidden from any other class and can be accessed only through any member function of own class in which they are declared.
- As in encapsulation, the data in a class is hidden from other classes using the data hiding concept which is achieved by making the members or methods of class as private and the class is exposed to the end user or the world without providing any details behind implementation using the abstraction concept, so it is also known as combination of data-hiding and abstraction..
- Encapsulation can be achieved by: Declaring all the variables in the class as private and writing public methods in the class to set and get the values of variables.
The whole
idea behind encapsulation is to hide the implementation details from users. If
a data member is private it means it can only be accessed within the same
class. No outside class can access private data member (variable) of other
class.
However if
we setup public getter and setter methods to update (for example void
setSSN(int ssn))and read (for example int getSSN()) the private data
fields then the outside class can access those private data fields via public
methods.
We can
create a fully encapsulated class in Java by making all the data members of the
class private. Now we can use setter and getter methods to set and get the data
in it.
The Java
Bean class is the example of a fully encapsulated class.
By providing
only a setter or getter method, you can make the class read-only or
write-only. In other words, you can skip the getter or setter methods.
It provides
you the control over the data. Suppose you want to set the value of id
which should be greater than 100 only, you can write the logic inside the
setter method. You can write the logic not to store the negative numbers in the
setter methods.
It is a way
to achieve data hiding in Java because other class will not be able to
access the data through the private data members.
The
encapsulate class is easy to test. So, it is better for unit testing.
Example
of Encapsulation in Java
How to
implement encapsulation in java:
1) Make the instance variables private so that they cannot be accessed directly
from outside the class. You can only set and get values of these variables
through the methods of the class.
2) Have getter and setter methods in the class to set and get the values of the
fields.
class EncapsulationDemo{
private int ssn;
private String empName;
private int empAge;
//Getter and Setter methods
public int getEmpSSN(){
return ssn;
}
public String getEmpName(){
return empName;
}
public int getEmpAge(){
return empAge;
}
public void setEmpAge(int newValue){
empAge = newValue;
}
public void setEmpName(String newValue){
empName = newValue;
}
public void setEmpSSN(int newValue){
ssn = newValue;
}
}
public class
EncapsTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
EncapsulationDemo obj = new EncapsulationDemo();
obj.setEmpName("Mario");
obj.setEmpAge(32);
obj.setEmpSSN(112233);
System.out.println("Employee
Name: " + obj.getEmpName());
System.out.println("Employee SSN:
" + obj.getEmpSSN());
System.out.println("Employee Age:
" + obj.getEmpAge());
}
}
Output:
Employee Name:
Mario
Employee SSN:
112233
Employee Age:
32
In above example all the three data members (or data fields) are private(see: Access Modifiers in Java which cannot be accessed directly. These fields can be accessed via public methods only. Fields empName, ssn and empAge are made hidden data fields using encapsulation technique of OOPs.
Advantages
of Encapsulation:
- Data Hiding: The user will have no idea
about the inner implementation of the class. It will not be visible to the
user that how the class is storing values in the variables. He only knows
that we are passing the values to a setter method and variables are
getting initialized with that value.
- Increased Flexibility: We can make the variables of
the class as read-only or write-only depending on our requirement. If we
wish to make the variables as read-only then we have to omit the setter
methods like setName(), setAge() etc. from the above program or if we wish
to make the variables as write-only then we have to omit the get methods
like getName(), getAge() etc. from the above program
- Reusability: Encapsulation also improves the
re-usability and easy to change with new requirements.
- Testing code is easy: Encapsulated code is easy to
test for unit testing.
Encapsulation
simply means binding object state(fields) and behaviour(methods) together. If
you are creating class, you are doing encapsulation.


Comments
Post a Comment